Energy Label
Polysun can calculate the Energy label for one of your system diagrams according to the EU regulations 811/2013 and 812/2013.
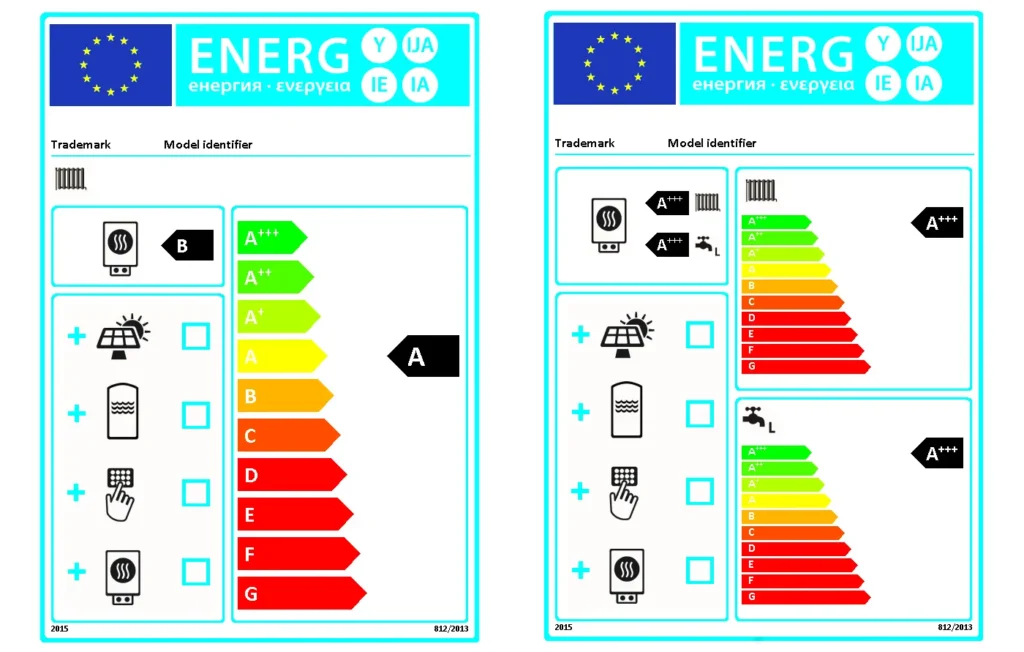
The Energy label can be calculated for systems with space heating and/or domestic hot water preparation. A separate energy efficiency class will be calculated for both space heating and domestic hot water preparation. The calculation results can be found in the attached data sheets.
You can instantly access the Energy label under “Results – Energy label”. This option also allows you, to save the label and the data sheets as an image file (*.png) and to enter additional parameters.
The Energy label can be part of both the short report and the professional report. The short report includes the Energy label, the professional report incorporates both the Energy label and the pertaining data sheets. Additionally, the section “System overview” will display the energy efficiency classes for domestic hot water preparation and space heating. You can choose whether you want the label displayed in the report or not under “Options – Settings – Report”.
Preconditions for the Calculation of the Energy Label
The Energy label can only be calculated for the some system types:
- The main heat generator of the system needs to have a nominal power of less than 70 kW. This main heat generator may be a boiler, a heat pump, a cogenerator or an internal heat generator in a storage tank (electric resistance heater).
- An Energy label can be calculated only for boilers fueled by oil, gas or electricity. It cannot be calculated for boilers using firewood or pellets as fuel.
- The system may include an additional heat generator, provided it is a boiler or an internal heat generator in a storage tank. If the additional heat generator is a heat pump or a cogenerator, the Energy label cannot be calculated.
- For systems that include more than two heat generators, no Energy label can be calculated.
- The system may only include one collector field with solar thermal or PVT collectors. A system including a collector field must also include a storage tank.
- The system may include no more than three storage tanks.
- If the system is designed only for domestic hot water preparation and not for space heating, an Energy label can only be calculated if the storage tank volume is less than 500 liters.
Calculation of Energy Efficiency Classes
The following parameters enter into the calculation of the energy efficiency class for space heating:
- the energy efficiency of the heat generator used for space heating,
- class of the temperature control,
- energy efficiency of the additional heat generator, if applicable,
- data of collector and storage tank, if applicable.
The following parameters enter into the calculation of domestic hot water preparation:
- the load profile selected for hot water consumption,
- the energy efficiency of the heat generator used for domestic hot water preparation in the selected load profile,
- data of collector and storage tank, if applicable.
Data relating to the storage tank are only relevant if the system includes a collector field. Otherwise, they are not entered into the calculation.
Components
Heat Generator
The following data of the heat generator enter into the calculation:
- Nominal power,
- Space heating energy efficiency,
- Domestic hot water preparation energy efficiency.
The values for space heating and domestic hot water preparation efficiency are recorded values that should be part of the catalog. In the case that the catalog does not include these values (yet), Polysun will calculate approximations.
Domestic Hot Water Load Profile
According to the EU regulation, there are four load profiles relevant for the calculation of the Energy label:
Table: Load profile according to EU regulation
| Load profile | Energy used for domestic hot water preparation |
| M | 5.845 kWh/d |
| L | 11.655 kWh/d |
| XL | 19.07 kWh/d |
| XXL | 24.53 kWh/d |
The load profile can be determined in the “Hot water demand” dialogue. It can either be entered manually or calculated automatically using the yearly demand.
Temperature Control
According to the EU regulation, there are eight classes of temperature control:
Table: Classes of temperature control according to EU regulation
| Class | Description | Correction factor |
| I | On/off room thermostat | 1 % |
| II | Weather compensator control, for use with modulating heaters | 2 % |
| III | Weather compensator control, for use with on/off output heaters | 1.5 % |
| IV | TPI room thermostat, for use with on/off output heaters | 2 % |
| V | Modulating room thermostat, for use with modulating heaters | 3 % |
| VI | Weather compensator and room sensor, for use with modulating heaters | 4 % |
| VII | Weather compensator and room sensor, for use with on/off output heaters | 3.5 % |
| VIII | Multi-sensor room temperature control, for use with modulating heaters | 5 % |
The temperature control class can be set when the Label is shown using the “Additional Parameters” tab. Temperature controls in Germany, Austria and Switzerland usually fall in the class VI type, so this is set as the default setting.
Storage Tank
The following data of the storage tank enter into the calculation:
- Storage tank volume,
- Standing losses.
The storage tank volume is usually the nominal volume taken from the storage tank-catalog. If for purposes of Energy label calculations a deviating volume should be considered, it can be entered into the column “volume (energy label)” of the catalog.
The standing losses can be found in the storage tank-catalog in the column “Standing losses”. It is defined as the heat loss of the entire storage tank measured in Watts and for 45 degrees Kelvin of temperature difference between the mean temperature in the storage tank and the ambient temperature. This should be a recorded measurement. In the case that the catalog does not include this measurement (yet), Polysun will calculate an approximation of the standing loss based on the insulation of the storage tank.
Collector Field
The following data of the collector field are taken into account for the calculation:
- Total collector aperture area,
- Optical efficiency η0 at ΔT ( υM – υL ) = 0 K, υM being mean absorber temperature, υL being mean ambient temperature of the collectors in °C
- Heat transmission coefficient a1, based on the aperture area,
- Temperature-dependent heat transmission coefficient a2, based on the aperture area,
- Angle factor (IAM value) at 50 °.
Both the orientation and the tilt angle of the collector field are irrelevant.
Headline of the Energy Label
The headline used for the Energy label consists of the trademark and the model identifier of the system rated.
When the label is displayed, the trademark can be entered once the button “Additional parameters” is clicked on. The name used for the installation will be the one chosen for the system diagram.